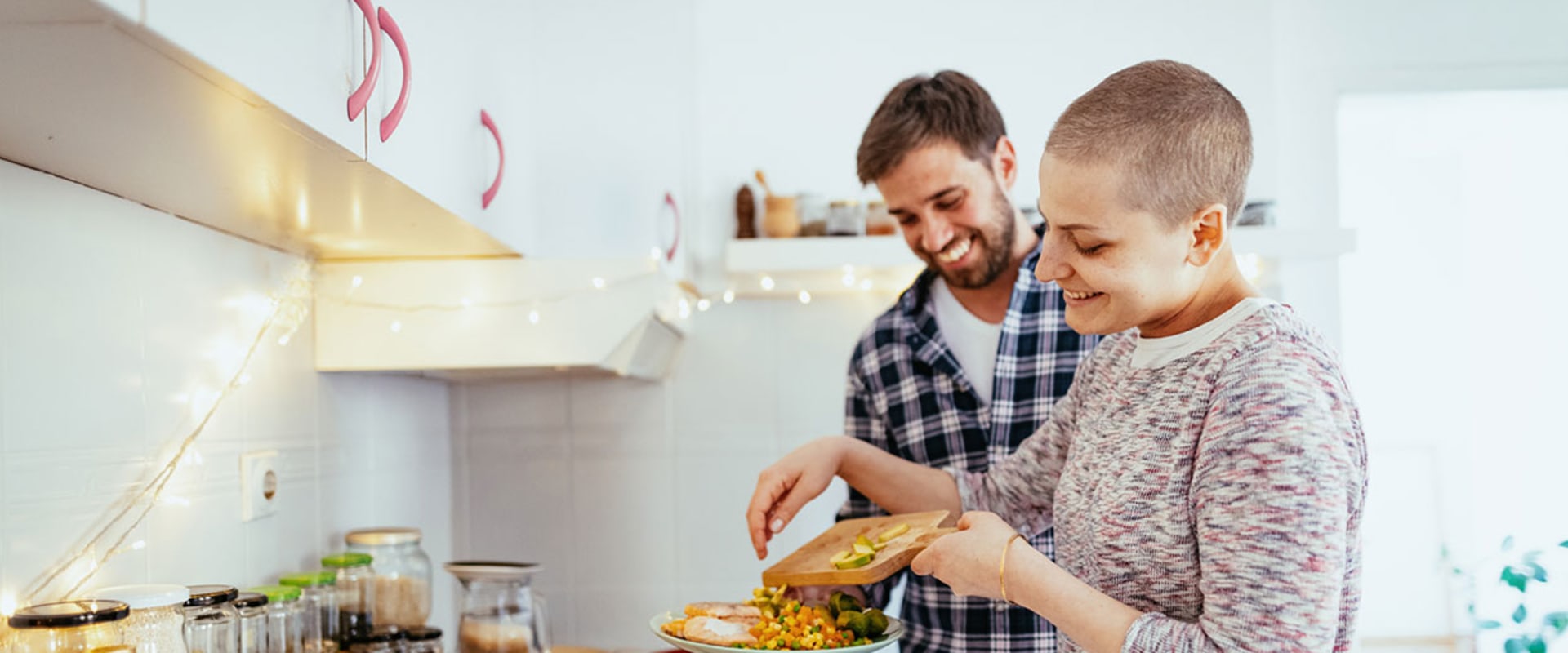
Eating plant-based meals is increasingly being recognized as an important part of a healthy lifestyle. As the evidence grows, we are learning more about the potential benefits of a plant-based diet for cancer prevention. In this article, we explore the evidence on how plant-based eating can help in reducing the risk of cancer, and provide tips for incorporating more plant-based foods into your diet. The power of plants lies in their nutrient density; they are packed with vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytochemicals that can help protect against chronic diseases such as cancer. Research has shown that a diet rich in whole plant foods is associated with a reduced risk of certain types of cancer, including colon, breast, and prostate cancer.
Plant-based diets are also linked to a lower risk of mortality from cancer and other chronic diseases.
Health Benefits of Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets have been linked to a variety of health benefits, including weight loss, reduced cholesterol levels, and improved heart health. Eating a plant-based diet means including more whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds in your meals. Weight loss is one of the most commonly reported benefits of switching to a plant-based diet. Plant-based foods are generally lower in calories than their animal counterparts, making it easier to cut back on calories and lose weight.In addition, plant-based diets are high in fiber, which helps to keep you feeling full longer and can help you stay on track with your weight loss goals. Eating a plant-based diet can also help to reduce cholesterol levels. Studies have shown that plant-based diets can help lower cholesterol by up to 10%. This is due to the fact that plant-based foods are naturally lower in saturated fat and cholesterol.
Finally, eating a plant-based diet has been linked to improved heart health. A plant-based diet is rich in antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, two major risk factors for heart disease. In addition, plant-based foods are naturally low in sodium, which helps to reduce blood pressure.
Tips for Transitioning to a Plant-Based Diet
Making the transition to a plant-based diet can be a daunting task, but it doesn't have to be.With a few simple tips, you can make the transition easier and more enjoyable.
Focus on Whole Foods
– When transitioning to a plant-based diet, it's important to focus on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help reduce your risk of cancer and other chronic diseases.Cookbooks, Websites, and Apps
– There are plenty of cookbooks, websites, and apps that can help you learn how to make delicious plant-based meals.From simple recipes to more complex dishes, there's something for everyone. You can also find meal plans and grocery lists that make it easier to stick to your plant-based diet. Making the transition to a plant-based diet doesn't have to be difficult. With a few simple tips and the right resources, you can make the switch to a healthier lifestyle easier and more enjoyable.
Types of Plant-Based Diets
When it comes to plant-based diets, there are a few different types to choose from. The three main types of plant-based diets are vegan, vegetarian, and flexitarian. Each of these diets has its own set of guidelines that determine what foods you can and cannot eat. A vegan diet is one where no animal products or by-products are consumed. This includes meat, eggs, dairy, and fish.Vegans also avoid honey, gelatin, and other animal-derived ingredients. When it comes to plant-based food, vegans eat a wide variety of vegetables, fruits, grains, nuts, and seeds. A vegetarian diet is one where no animal flesh is consumed. This includes all types of meat, fish, and poultry. However, some vegetarians do consume eggs and dairy products.
As with vegan diets, vegetarians can get their nutrition from a variety of plant-based foods. Finally, a flexitarian diet is one where a person follows a mostly plant-based diet but occasionally consumes animal products. This type of diet allows for more flexibility and is often used as an intermediate step for those transitioning to a vegan or vegetarian diet. Overall, the type of plant-based diet you choose should be based on your individual needs and preferences. All of these diets have their own benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to research each one carefully before making a decision. In conclusion, plant-based diets are an effective way to reduce your risk of cancer and other chronic diseases. They are also associated with many other health benefits, such as weight loss and improved heart health.
Transitioning to a plant-based diet can be challenging, but there are numerous resources available to help you get started. Eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes can help you make the switch to a plant-based diet, while also reducing your risk of cancer and other chronic diseases.